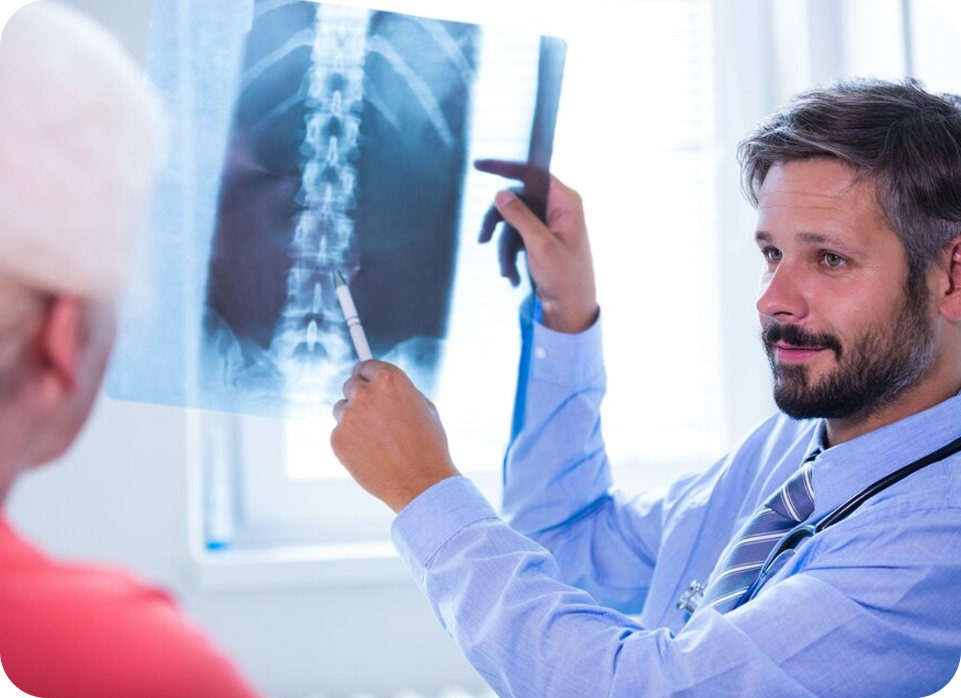
X-RAY
X-ray imaging is a diagnostic technique that uses ionizing radiation to produce images of the body's internal structures, particularly bones. It is one of the most commonly used imaging methods due to its ability to quickly and effectively visualize fractures, infections, and other abnormalities. X-rays work by passing radiation through the body, which is absorbed at different rates by various tissues, creating an image on a photographic film or digital detector.
Advancements in X-ray technology, such as digital radiography and computed tomography (CT), have improved image clarity and diagnostic capabilities. Digital X-rays offer faster processing and enhanced image quality compared to traditional film-based methods. X-rays are essential for a wide range of medical conditions, from routine examinations to complex diagnostics. However, due to the use of ionizing radiation, minimizing exposure and following safety protocols are crucial to protect both patients and healthcare professionals.

